The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, the Earth rotates anti-clockwise, and we all need plenty of fruit and vegetables in our diets - these are simple facts of life.
Despite this, the overwhelming majority of Americans still aren't consuming enough.
In a 2019 survey, the CDC found that only 10% of adults eat the recommended 1.5–2 cup-equivalents of fruits and 2–3 cup-equivalents of vegetables a day, and only 12.3% eat enough fruit to stay healthy.
In addition to missing out on crucial vitamins and minerals, this is problematic because it means that most people are also falling short on phytonutrients - compounds helping fight disease and keep your body moving.
Here, we're going to talk about what this means, the benefits of phytonutrients, and what foods you can use to fuel your body.
Read on to learn how you can enrich your diet with plant-based compounds and why you should make it a priority.


The Good Stuff - Performance
-
One scoop will infuse your coffee with healthy ingredients
-
Ditch the bad stuff like sugar, dairy, and artificial creamers
-
Fights inflammation and supports skin and joint health
-
Makes your coffee taste great
What Are Phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients are a broad category of compounds found in plant-based foods. This umbrella term encompasses antioxidants, flavonoids, carotenoids, polyphenols, and more.
Different phytonutrients come from various plant sources and affect the body differently.
Because these chemicals come from plants, fruits and vegetables are the primary sources of phytonutrients. However, other plant-based foods also will give you these compounds.
Tea, for example, is an excellent source of phytonutrients, as are nuts, beans, and whole grains.
It's worth noting phytonutrients aren't necessary to keep you alive and moving.
This distinguishes them from the vitamins, minerals, and electrolytes that keep your body functioning. Phytonutrients are supplements.
That said, they still contain a bunch of health benefits you won't want to miss!
How to Tell if a Food is Phytonutrient-Rich
Phytonutrients are the main reason that plants are colorful. By assessing its color, you can generally tell whether a food has many of these chemicals.
If foods have deeper hues, they usually are richer in phytonutrients. Dark green vegetables like spinach or kale, melons, berries, and various spices are primary sources of these compounds.
While some foods rich in phytonutrients are white (like garlic), using color to assess roughly how phytonutrient-rich a vegetable may be is a solid rule of thumb.
Plant-based foods that are more flavorful are also likely to have more phytonutrients than blander ones. Bold and easily-identifiable flavors are a sign of these chemical compounds—the more unique and distinguished the taste, the greater the benefits.
The Overarching Benefits of Phytonutrients
It's thought there are roughly 4000 kinds of phytonutrients. They all come with different properties and therefore vary in their health advantages. But there are many overarching benefits to consuming a phytonutrient-rich diet that everyone should know.
A study published by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) assessed those who consumed various dietary phytonutrients over time. They aimed to provide a scientific basis for the claim that those who eat more phytonutrient-rich fruits and vegetables are less susceptible to chronic illness.
The research project spanned five years and ultimately concluded that phytonutrient-rich foods may help stave off chronic illnesses. Cancer and heart disease are among the issues that people may be at lower risk for. This is especially true when the foods underwent natural post-harvesting processes.
This isn't the only study to analyze the broad impacts of phytonutrients on health.
In 2022, researchers assessed the impact of phytonutrients on gut health and found that they may increase human metabolism and digestive wellness. They interact with microbes in the gut to better trigger responses within the stomach, make it more responsive to stimuli, and potentially mitigate metabolism and stomach issues.
A 2011 study also showed that phytonutrients' antioxidant properties might protect against oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. This reduces the risk of pain in the joints, arteries, and muscles. It also means that people may be less susceptible to bone issues like osteoporosis and atherosclerosis.
This same study also found that many phytonutrient-rich fruits can improve blood vessel function and may protect against artery diseases.
Lower inflammation levels impact the body in many ways so that you can benefit your bone health and cardiovascular system in one fell swoop!
The Types of Phytonutrients
Understanding what different compounds can do for you can get you the information you need to balance your diet. Even beyond following Harvard University's healthy eating plate, you should know how to distribute fruits, veggies, and nuts in ways that make sense.
Up until this point, we've discussed phytonutrients holistically. But they're not a monolith, and there are several primary phytonutrient types that people should know about. While all phytonutrients have antioxidant qualities, each of them plays a more specific role in health as well.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are one of the biggest groups of phytonutrients. There are hundreds of flavonoid types divided into several different subcategories. Some of the most common categories are flavones, flavonols, anthocyanins, and isoflavones.
All of these compounds contribute to communication between healthy cells throughout your body. Per a 2014 study, they moderate pathways between cells that help them to survive. They also have neuroprotective properties and allow signaling pathways in the cell system to work together better.
This cell communication can decrease inflammation. It also can trigger detoxification, which naturally cleanses your blood of harmful toxins. In some cases, flavonoids may also slow the spread of tumors and reduce the risk of cancer development.
Because flavonoids are so diverse, they're also prevalent in many foods. Some of the most common things you can use to get some into your diet are:
- Apples
- Onions
- Green tea
- High-quality coffee
- Ginger
- Onions
- Tart cherry
Carotenoids
If you see brightly-colored fruits and veggies, they probably contain carotenoids. That's because carotenoids are pigments that give plants a bright green, orange, red, purple, or other vivid hue.
There are over 600 carotenoid types. Some common ones include alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, lycopene, and zeaxanthin.
There are many benefits to consuming carotenoids, including immune system support. Studies suggest that those who eat a healthy amount of these compounds will have better immune cell function. This may prevent colds but also stave off chronic diseases, including cancer.
Carotenoids are also heavily associated with Vitamin A, responsible for eye health. Lutein and zeaxanthin are two of the most common carotenoids, and they are naturally found in the retina of your eye.
Supplementing this compound may decrease the risk of eyesight loss and macular degeneration.
Common sources of carotenoids include carrots, spinach, pumpkins, beets, kale, oranges, and sweet potatoes.
Glucosinolates
There are many reasons to consume foods containing glucosinolates, as they're thought to help combat inflammation and disease.
Rat studies have also suggested that glucosinolates can be broken down to make carcinogens inactive. This protects cells in the body from DNA damage that could cause cancer in the long run. While we're still waiting on human studies to give us more information, this could be a significant discovery on the road to combating cancer.
Glucosinolates are primarily found in cruciferous veggies like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, bok choy, and Brussels sprouts.
You also can find glucosinolates in mustard, so think about that next time you head to the condiment station!
Ellagic Acid
Ellagic acid is a phytonutrient most common in colorful fruits. Ellagic acid can decrease your cholesterol in addition to having anti-inflammatory qualities.
Some studies have even suggested that ellagic acids may halt the development of atherosclerosis. Since this condition causes fatty materials to develop around the arteries, ellagic acid can stop you from experiencing inflammation-related pain. It can also make your blood flow healthier and potentially combat cardiovascular problems like heart disease.
If you're looking to add come ellagic acid to your diet, you're in luck. Tons of the tastiest treats contain this incredible compound, including raspberries (which have one of the highest concentrations of ellagic acid), strawberries, blackberries, pomegranate seeds, and grapes (both green and purple varieties).
You can also get ellagic acid from walnuts and pecans, offering you a protein boost in addition to the benefits of phytonutrients!
Resveratrol
In addition to ellagic acid, resveratrol is an abundant compound in grape skins (yep, even in red wine!).
This phytonutrient supports cardiovascular health. Studies show that it may combat the risk of cardiovascular disease and heart failure. This makes it a traditional and natural way to stay in shape and regulate your heart health.
This compound is also heavily associated with cognitive health. It boosts the blood flow to your brain so that you can stay energized, develop a better memory, and focus on day-to-day tasks.
If you're looking to get resveratrol without grapes, you can also try berries, peanuts, and dark chocolate.
Yes, you read that right. Chocolate, specifically dark chocolate, can help boost your heart health and cognitive function! Just ensure you get natural chocolate snacks without artificial colors and preservatives.
How to Get More Phytonutrients
Now that you know some properties of various phytonutrients, it's time to understand how to get more of them into your diet. This may sound straightforward, but there are a lot of considerations you need to consider before you start meal planning.
Diversify Your Plate
To get as much goodness from your food as possible, it's essential to diversify your plate's "fruits and vegetables" section. Roughly half of every meal should be made up of fruits and veggies, but you don't want to eat the same thing every time you sit at the table.
Mix green vegetables like broccoli with other brightly-hued ones like carrots and squash. This will ensure that you get carotenoids as well as flavonoids. Adding beans and legumes will also help you get other compounds, so try switching things up now and then.
You also will want to try lots of delicious fruits.
Raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries are easy to eat as snacks or side dishes. They'll give you ellagic acid. Grapefruits and oranges are excellent sources of flavonoids and phytoestrogens.
Experiment a bit and add fruit to breakfast recipes like an apple and cinnamon bircher muesli, or try tart cherries for dessert.
Boost Your Daily Cup of Coffee
Coffee is also an excellent way to get flavonoids, and it has other health benefits to boot.
Quality Arabica coffee can help boost your energy, support focus, enhance your memory, and generally improve your cognitive function.
The only problem with coffee is that many of us negate its benefits with artificial sugars, creams, and sweeteners.
However, you can replace this bad stuff with coffee supplements like The Good Stuff™.
Not only are you cutting out the calories and the artificial nasties, but each scoop contains cinnamon, full of the phytonutrient cinnamaldehyde.
Cinnamaldehyde is thought to help combat inflammation - plus, it makes your coffee taste delicious!
Get a Concentrated Dose of Phytonutrients
Just want the phytonutrients without having to overhaul your diet altogether?
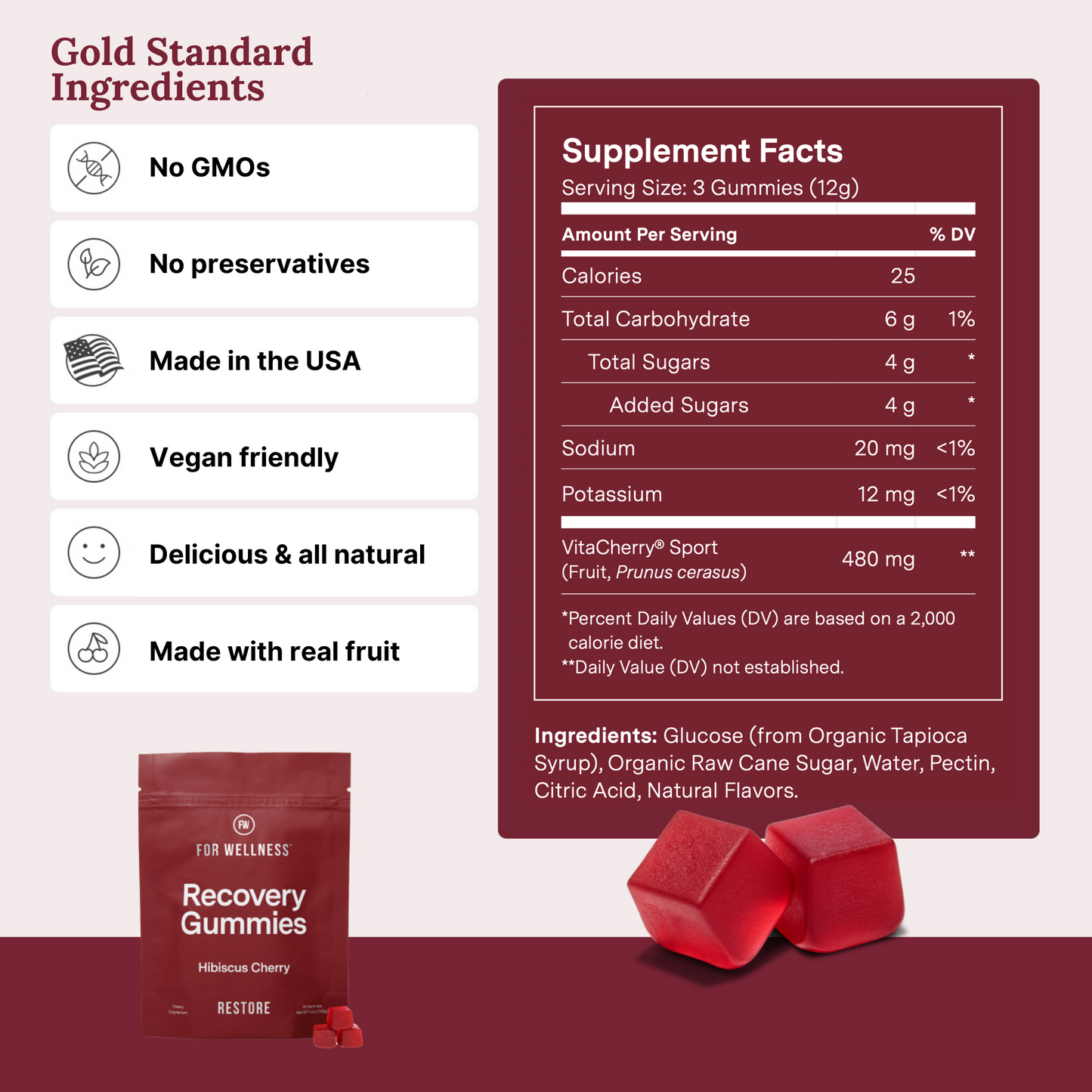
Our Recovery Gummies™ are derived from Montmorency tart cherries, delivering the full complement of phytonutrients from tart cherries in a delicious gummy.
Tart cherries can also help benefit athletes by protecting against muscle soreness and strength loss and aiding in muscle recovery.
Each gummy also contains electrolytes for hydration and glucose for rapid energy, perfect for on-the-go!
Talk to Your Doctor
As with all health-related switches, you can talk to a medical professional if you need help with how to add phytonutrients to your diet.
Asking your doctor at your next physical exam or routine visit can help ease your mind while changing your diet to be healthier.
You also can talk to a diet specialist for tips and tricks on balancing the phytonutrients on your plate. This will help you be more confident that you're making suitable dietary switches.
Beyond Plant-Based Compounds
As you now know, consuming phytonutrients is a natural and science-backed way to support your health.
Now that you're across the basics of phytonutrients and where they come from, it's time to get started. See what small changes you can make to your diet to help your body reach its full potential.
We're Here to Help
At For Wellness, we're committed to helping people replace the unhealthy parts of their diet with better alternatives.
We offer snack bars and coffee supplements to keep you feeling energized and well-fueled throughout the day.
We also are excited to share recipes and health tips with you!
If you have any questions about us or any of our products, we're only an email away.