Disclaimer: This article is for general information only and should not replace professional medical care. If you have any questions or concerns about your health, speak to your physician.
Here at For Wellness, we talk a lot about the anti-inflammatory properties of The Good Stuff, FOCUS, and coffee. When most people hear the term inflammation, they probably think about swollen cuts and painful joints.
However, it’s also a chronic issue that could affect you without your knowledge. The impacts of inflammation on things like your joints, stomach, and other crucial organs can have major ramifications for your health while being an extremely tricky issue to nail down. That’s why it’s important to do what you can to limit inflammation and be mindful of some of its symptoms.
The good news is one of the easiest and most effective ways of combating inflammation is through your diet, so we’ve compiled a quick guide of some things of which to be mindful.
In this article, we’ll cover anti-inflammatory and inflammatory foods, the impact of reducing inflammation, symptoms of inflammation, people who are most likely to suffer from inflammation, and the effect of inflammation on your health and well-being.


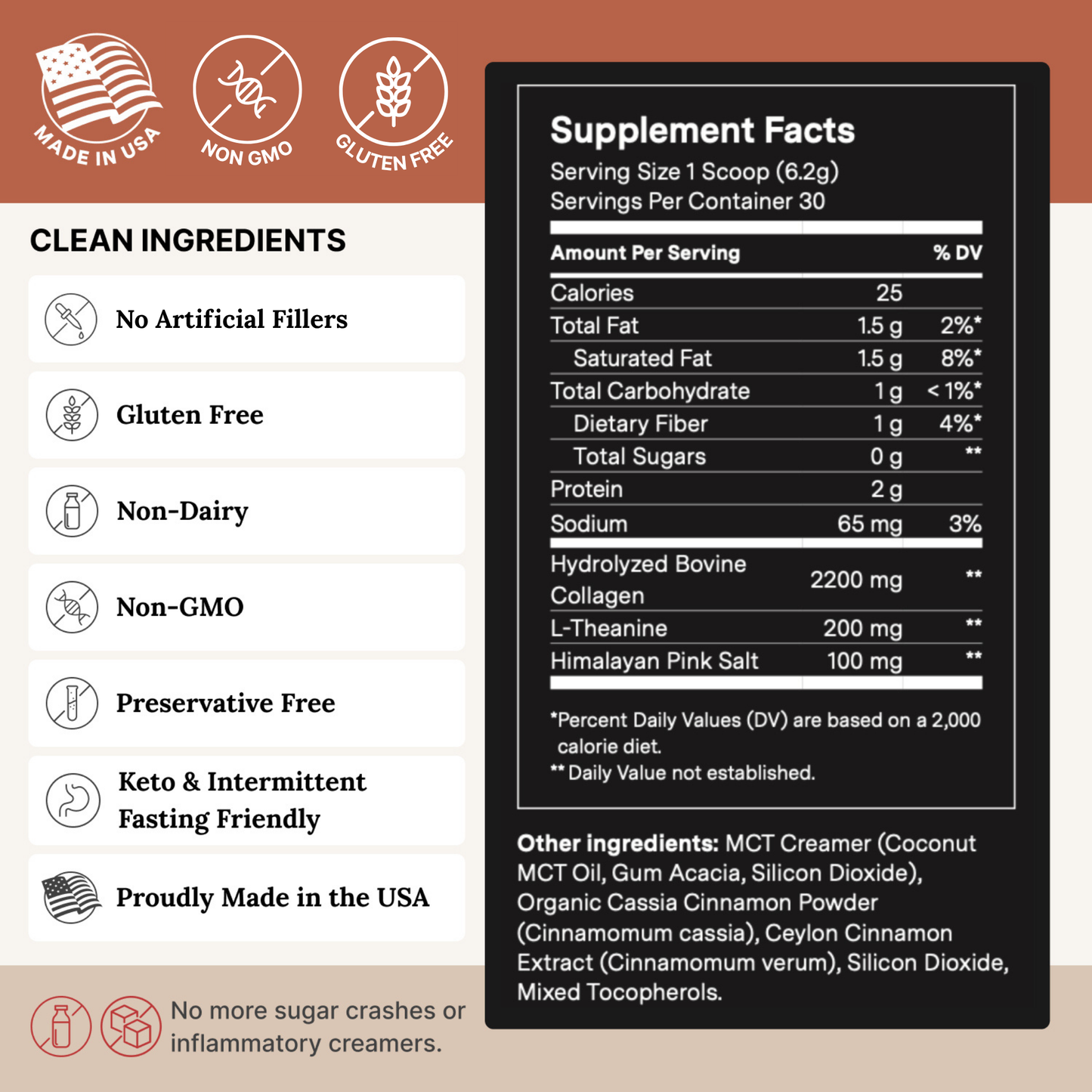
The Good Stuff - Performance
-
One scoop will infuse your coffee with healthy ingredients
-
Ditch the bad stuff like sugar, dairy, and artificial creamers
-
Fights inflammation and supports skin and joint health
-
Makes your coffee taste great
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, which works by dispatching white blood cells to the affected area to attack bacteria and heal damaged tissue.
This response may continue for a prolonged period or be triggered unnecessarily, causing various health problems. For example, chronic inflammation has been linked to heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
The Importance of Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation comes in a range of forms, from stomach inflammation (AKA gastritis) to inflammation of the joints, to acute inflammation of individual areas of the body.
Reducing inflammation is important because it can help alleviate symptoms of chronic diseases and improve overall health. By decreasing inflammation, the body can better regulate its immune response, enhancing organ and system function.
Additionally, reducing inflammation can help prevent the development of chronic diseases by promoting a healthy immune response and reducing the stress on the body that can contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
Symptoms of Inflammation
Symptoms of inflammation can vary depending on the cause and location of the inflammation. Common symptoms of inflammation include redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function.
Who is most likely to suffer from inflammation?
- People with chronic health conditions like obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders are more likely to suffer from chronic inflammation.
- Those with a poor diet high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats may also be at a higher risk for inflammation.
- Stress, lack of sleep, and a sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Aging can also increase the risk of inflammation as the body’s immune system weakens.
It’s important to note that anyone can suffer from inflammation, regardless of age or health status. That’s why we must maintain a healthy lifestyle and diet to reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and associated health problems.
Here’s a short list of some of the most accessible anti-inflammatory foods you can add to your diet to combat inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory foods
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation by blocking the production of certain enzymes that promote inflammation.
- Berries: Berries like strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants, plus they’re a good source of fiber, which can help promote gut health and reduce inflammation.
- Coffee: Coffee contains several compounds that have anti-inflammatory properties, including polyphenols and chlorogenic acid. Polyphenols are antioxidants that can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Coffee also contains caffeine, which can have anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of specific cytokines that promote inflammation.
- Cinnamon: This over-achieving spice contains compounds called cinnamaldehyde and eugenol, which can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, while eugenol inhibits the activity of an enzyme that triggers inflammation. Cinnamon can be great for helping ease inflamed joints.
- Leafy greens: Leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens are high in vitamins and minerals, which can help reduce inflammation.
Inflammatory foods
- Fried foods: Processed foods like chips, crackers, and fast food are high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives, promoting inflammation in the body.
- Sugary drinks: Sugary drinks like soda and some sports drinks are high in sugar, which can promote inflammation in the body.
- Red meat and processed meat: Red meat is high in saturated fat, which can promote inflammation. Processed meats like bacon and sausage are also high in additives, which can promote inflammation.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol use can undermine gut and liver functions and multi-organ interaction, causing ongoing inflammation and - if unchecked - potential organ damage.
You’ve probably noticed a clear pattern here: anti-inflammatory foods are also foods that are overall healthier, whereas inflammatory foods are those full of sugars, unhealthy fats, processed carbs, and additives.
While we know we need to eat these foods, it can be challenging to incorporate them into our daily diet.
And that's where we come in!
We’ve made it extremely easy for you to make healthy choices. Try replacing your sugary syrups and creamers in your coffee with The Good Stuff™ or The Good Stuff™ FOCUS, and not only are you removing an inflammatory substance, but you’ll get the benefits of coffee and cinnamon in your daily diet.
Take that, inflammation!