Walk into any wellness or health food store, and you'll likely find an array of collagen pills, powders, and creams lining the shelves.
These products say they'll turn back the hands of time, giving you more youthful skin, stronger hair, and improved joint health. But what exactly is collagen, how does it work, and does it live up to its claims?
This article will dig into those questions and more. Here's what you need to know about this vital protein.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a structural protein that acts as the glue that holds your body together, quite literally!
The word originates from the Greek word "kólla," or glue.
It's the most abundant protein in humans—comprising about 30 percent of your body's total protein—and makes up a substantial portion of your skin, hair, nails, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones.
Collagen is essential for maintaining the structural integrity and elasticity of these various components. At its core, collagen is composed of 18 amino acids and is particularly high in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.


The Good Stuff - Performance
-
One scoop will infuse your coffee with healthy ingredients
-
Ditch the bad stuff like sugar, dairy, and artificial creamers
-
Fights inflammation and supports skin and joint health
-
Makes your coffee taste great
These amino acids are the building blocks of protein and play a critical role in collagen's unique structure. Collagen molecules form long chains that intertwine with one another, creating a strong and flexible framework.
Types of Collagen
There are 28 different forms of collagen, each differing by how the molecules are assembled and where the collagen is used in the body.
The three main collagen types include:
Type I Collagen: Found in skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, and organs, Type I collagen provides strength and support to these structures and maintains skin's firmness and elasticity.
Type II Collagen: Predominantly present in cartilage, Type II collagen is crucial for maintaining joint health and flexibility. It cushions and protects the joints, making movements smooth and pain-free.
Type III Collagen: This type is often found in skin, blood vessels, and organs. It works in conjunction with Type I collagen to enhance the skin's suppleness and helps maintain the integrity of blood vessel walls.
How Is Collagen Made?
The human body naturally produces collagen, however, as you age, your body produces less collagen. Starting in your mid-20s, you typically lose about 1 percent of your collagen yearly. This decrease in collagen is one of the primary factors contributing to visible signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles, as well as the gradual loss of joint flexibility and bone density.
Certain lifestyle factors can also accelerate collagen breakdown. These include:
- A high-sugar diet
- Spending too much time in the sun (don't forget your sunscreen!)
- Smoking
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Not getting enough sleep
Recognizing the importance of collagen, the wellness and beauty industries have introduced collagen supplements to the market to help supplement what's lost. These supplements are produced by extracting collagen proteins from various animal sources, such as bovine (cow), porcine (pig), and marine (fish).
What Are the Health Benefits of Collagen Supplements?
Because collagen is one of the most abundant proteins in the body, the range of potential benefits associated with collagen supplementation is extensive and varied.
Let's take a look.
#1: Improved Skin Health
One unfortunate reality of aging is developing wrinkles and saggy skin, and at the heart of this inevitable transformation is the gradual loss of collagen.
Fortunately, several studies have shown that collagen supplements can help reduce signs of skin aging. One review of 11 studies involving mostly women found that taking 3-10 grams of collagen daily for an average of 69 days led to improvements in skin elasticity and skin hydration.
Researchers think these benefits may stem from the ability of collagen supplements to stimulate natural collagen production. Another theory is that collagen supplements may promote the production of other proteins that support the structure of the skin, including elastin and fibrillin.
What about topical collagen creams? While a cream might moisturize your skin, that's about all it will do. Collagen creams have not been shown to stimulate collagen synthesis.
#2: Reduced Joint Pain
Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of your cartilage—a strong yet flexible connective tissue that protects your joints and bones. As the natural collagen levels in your body gradually diminish with age, your susceptibility to conditions stemming from cartilage deterioration, such as osteoarthritis, increases.
A review of studies in people with osteoarthritis found that taking collagen significantly improved joint stiffness and overall symptoms.
In another study involving 60 people with severe, active rheumatoid arthritis, consuming collagen for three months decreased the number of swollen and tender joints.
Even more impressive, four participants in the collagen group went into complete remission.
Some researchers have theorized that supplemental collagen may accumulate in cartilage, prompting the body to increase its own collagen production. This increase may lead to lower inflammation, better joint support, and reduced pain.
#3: Reduced Bone Density Loss
Your bones are primarily made up of collagen, which gives them structure and strength. As collagen diminishes with age, so does the density and strength of your bones.
This decline in bone health can pave the way for conditions like osteoporosis, marked by reduced bone density and an elevated susceptibility to fractures. Collagen holds promise here, too—studies show that supplemental collagen may help prevent the bone breakdown that leads to osteoporosis.
#4: Increased Muscle Mass
Collagen plays a crucial role in the composition of skeletal muscle. But as you age, you gradually lose muscle mass. One possible antidote for this is collagen supplements, as studies suggest they may help boost muscle mass in people with sarcopenia (the loss of muscle mass that happens with age).
A notable 12-week study involved 27 older men grappling with this condition. The men took 15 grams of collagen while participating in an exercise program. They gained significantly more muscle mass than men who exercised but did not take collagen.
This benefit may stem from supplemental collagen's ability to promote the synthesis of muscle proteins like creatine and boost muscle growth after exercise.
#5: Improved Heart Health
Collagen provides structure to your arteries, which are tube-like structures that transport blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Without enough collagen, your arteries become less flexible and elastic. This can lead to a disease called atherosclerosis, which is characterized by narrowing of the arteries. Over time, atherosclerosis can lead to heart attack and stroke.
In a six-month study, 31 healthy adults took 16 grams of collagen daily. During the study period, they experienced a significant reduction in measures of artery stiffness. On top of that, their levels of HDL (good) cholesterol increased by an average of 6 percent.
#6: Healing Leaky Gut
Research is new in this area, but some exciting cell and animal studies are looking at collagen's benefits for gut health.
One study, which used cell models designed to simulate the human gut environment, yielded promising results.
It revealed a decrease in gut permeability (referred to as "leaky gut") and a reduction in inflammation.
Another recent study explored the effects of fish collagen using a mouse model with human immune cells sourced from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients.
The results showed that the mice given collagen exhibited diminished gut inflammation and improved balance in their gut microbiota compared to their counterparts who did not receive collagen supplementation.
#7: Improved Nail and Hair Health
Supplementing with collagen can improve nail growth and reduce brittle nails. In one 24-week study, participants who incorporated a collagen peptides supplement into their routine experienced a 12 percent acceleration in nail growth rate and a 42 percent reduction in the occurrence of nail breakage.
Collagen supplements contain amino acids that your body can use to build keratin, a primary protein in hair. This may help stimulate hair growth and increase its strength.
How to Add Collagen to Your Diet
Adding collagen to your diet is a breeze. There are four ways to do so:
- Oral collagen supplements (in capsule form)
- Add collagen powder to smoothies, coffee and tea
- Consume collagen-rich foods, such as bone broth and skin-on chicken
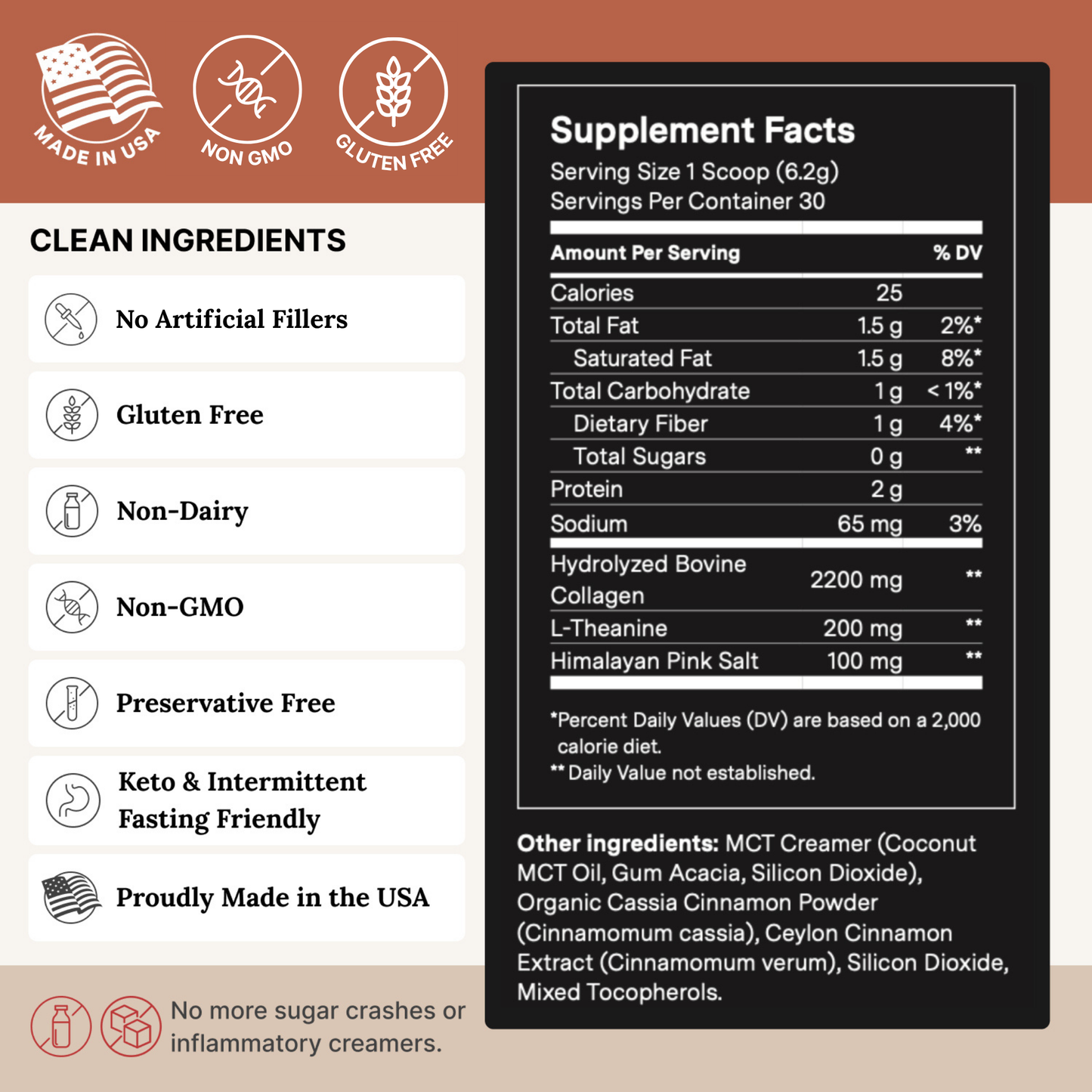
- Take a performance supplement that has collagen as one of several ingredients A super easy and tasty way to add collagen to your diet is with The Good Stuff™ or The Good Stuff™ Focus.
We use hydrolyzed collagen (from bovine sources) so it blends well and is perfect for adding to coffee, tea, or smoothies.
⚡️The Good Stuff™ also includes other performance-packed ingredients, including L-theanine, collagen, organic cinnamon, and C8-MCT, which collectively support cognitive function, mental clarity, energy, and mood.
☕️A scoop of The Good Stuff™ can easily replace artificial creamer and sweetener in your coffee and make your cup of joe one of the healthiest things you consume daily.
🧠Looking for an extra boost of focus? Try The Good Stuff™ Focus, which has the same performance ingredients as the original blend, plus theobromine—a cacao extract that can boost focus and learning.
Embrace the Age-Defying Power of Collagen
While collagen can't guarantee everlasting youth and immortality, its potential health benefits are well supported. So, whether you sip it in your morning coffee, blend it into your smoothie, or add it to your pancake mix, collagen is a reminder that wellness is not just about the years in your life but also the life in your years.
Written by Katie Koschalk, a health and wellness writer, certified holistic nutritionist, and certified personal trainer based in California.